Heat-foaming of volcanic glass particles in the pyroclastic deposit

Fig. Microphotographs on heating stage (Particle size: 0.2mm, Heating rate: 1000°C/min).
weathered surface layer in which Na+ is exchanged by H+
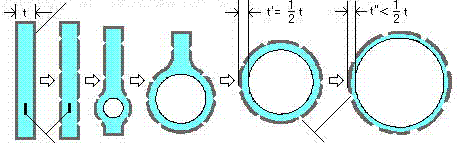
crystallite or impurity groove-like crack
1) 25°C 2) 500℃ 3) 900°C 4) 950°C 5)1000°C 6) end of foaming
Fig. Schematic model of foaming mechanism by heating.
| 1) | Natural particle is heated. |
| 2) | At about 500°C, some cracks appear on the surface by shrinkage of the surface layer according to volatilization of H2O molecules formed from H+ ions. |
| 3) | At about 900°C, the inner part is softened earlier than the surface layer, because of volatilization of H+ ions from the surface layer and the gradual increase of Na+ ions density from surface to inside. At the same time, bubble generates from the nucleus that is composed of an alien substance such as crystallites. |
| 4) | At about 950°C, bubble expands to the direction of fin-like edges, because the surface layer is harder than the inner part. |
| 5) | At about 1000°C, this hard layer becomes surface. The shape is formed spherical by the hard layer. |
| 6) | At the end of foaming, small groove-like patterns are formed on the surface by expansion of the sphere. |